 Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Overview
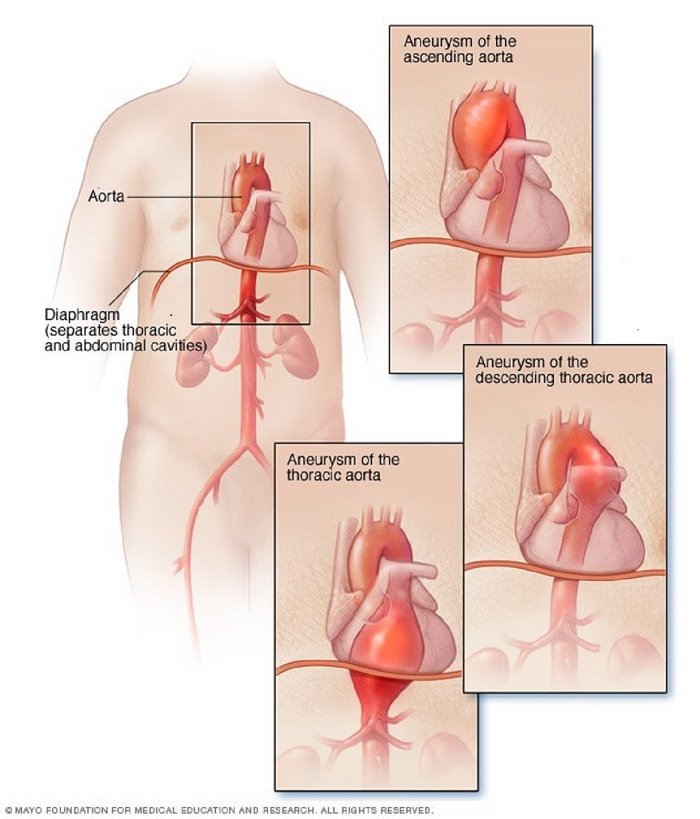
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is a weakened area in the upper part of the aorta — the major blood vessel that feeds blood to the body. Aneurysms can develop anywhere in the aorta.
Detailed imaging tests, such as transesophageal echocardiogram, CT angiogram and MRI angiogram to diagnose aortic aneurysms. The latest imaging tests are also used to look for tears in the inner layer of the aortic wall (aortic dissection) and determine the most appropriate treatment for your condition.
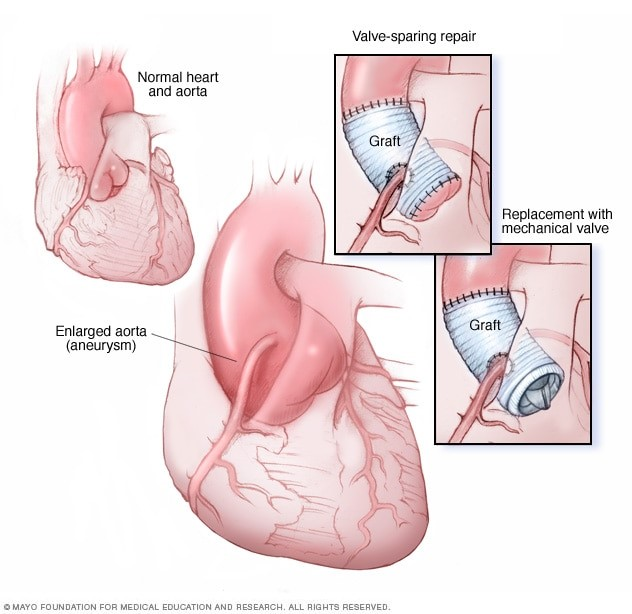
Several types of aortic root surgery, including:
- Aortic valve and root replacement: In aortic valve and root replacement (composite aortic root replacement), your surgeon removes a section of your aorta and your aortic valve. The section of your aorta is replaced with an artificial tube (graft), and your aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve. If you have a mechanical valve, you'll need to take anticoagulant medications for life to prevent blood clots.
- Valve-sparing aortic root repair:In this procedure, your surgeon replaces the enlarged section of your aorta with an artificial tube (graft). Your aortic valve remains in place. In one technique, your surgeon sutures the valve inside of the graft.
If you have certain other heart conditions, your surgeon may perform additional procedures to treat these conditions at the same time as aortic root surgery.
An ascending aortic root aneurysm procedure may be performed in two ways. In aortic root replacement, your surgeon removes a section of your aorta and your aortic valve, and replaces the section of the aorta with an artificial tube (graft). The aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical valve.
